1. Executive Summary
As organisations face increasing pressure to deliver technology rapidly, Enterprise Vibe offers a structured approach to implementing AI-driven development across large organisations, enabling faster innovation while maintaining governance and security. This comprehensive framework transforms traditional development methodologies into an AI-augmented paradigm that dramatically accelerates software delivery.
Enterprise Vibe represents a strategic shift in how organisations develop software, leveraging AI-assisted coding to dramatically accelerate development cycles while maintaining quality and security. This proposal seeks to communicate how to fundamentally transform operating models to achieve the following outcomes:
- Reduction of development time by 20%-80% through AI-assisted coding practices (depending on task type/complexity/individual personality traits).
- Improved resource utilisation by focusing human expertise on high-value activities.
- Enhanced product quality through rapid iteration and AI-driven quality assurance.
- Strengthened competitive position through faster time-to-market for new features and propositions.
The proposed implementation requires an initial investment of resources for tooling, training, and organisational restructuring, but projects a positive ROI within 12 months through development efficiency gains and reduced time-to-market. This document outlines the complete Enterprise Vibe operating model, implementation approach, and expected outcomes.
2. Introduction to Vibe Coding
Vibe coding is an AI-assisted software development approach where developers leverage artificial intelligence to generate, refine, and validate code. Rather than manually writing every line, developers interact with AI tools to describe functionality, iterate quickly, and focus on high-level problem-solving. This dramatically accelerates development speed, reducing the need for traditional backlog management and extensive manual coding.
The transformation from conventional coding to vibe coding represents a paradigm shift comparable to the adoption of agile methodologies two decades ago. By offloading routine implementation tasks to AI systems, developers can concentrate on architecture, business logic, and user experience - areas where human creativity and domain expertise add the greatest value. This realignment of human effort toward strategic aspects of development creates both efficiency gains and opportunities for innovation that were previously constrained by implementation bottlenecks.
3. What is Enterprise Vibe?
Enterprise Vibe extends the principles of vibe coding to large organisations by integrating governance, security, scalability, and structured team collaboration.
- AI-driven coding is the norm, but with human oversight where needed to maintain quality, security, and alignment with business objectives.
- Teams are optimised for collaboration, communication, and efficiency through structured workflows and clear role definitions.
- Governance structures enable rapid progress without sacrificing control and compliance, implementing guardrails rather than roadblocks.
- A centralised support system handles specialised needs and ensures alignment with enterprise standards, providing expertise where needed.
- Organisations can seamlessly transition from traditional software methodologies through comprehensive training and support programs.
Unlike isolated experiments with AI coding tools, Enterprise Vibe represents a holistic transformation that embeds AI throughout the development lifecycle while maintaining the governance and security controls required in enterprise environments. This approach creates a foundation for sustainable acceleration of development activities while addressing the organisational and compliance requirements unique to large enterprises.
4. Business Case & ROI Analysis
The business case for Enterprise Vibe rests on three primary value drivers: development acceleration, resource optimisation, and competitive advantage. Our analysis indicates the following financial impacts:
Initial Investment Requirements
- This depends on the scale of your organisation. The following costs should be factored:
- AI tooling and infrastructure
- Training and enablement
- Implementation and change management
Expected Returns
- Development efficiency gains: 20%-80% reduction in development hours
- Time-to-market acceleration: Features delivered in days rather than weeks
- Resource reallocation value: 20-25% of developer time redirected to high-value activities
- Quality improvement: 15-20% reduction in post-release defects
ROI Timeline
- The break-even point and long-term value depend on the size of the initial investment and the scale of the organisation. However, based on the implementation approach outlined in section 10, we predict a break-even point in 6-9 months.
Opportunity Cost of Inaction
- Continued competitive disadvantage in release velocity
- Increasing technical debt from manual coding practices
- Higher recruitment costs in competitive developer market
- Missed opportunities for AI-driven innovation
This analysis demonstrates that while Enterprise Vibe requires significant initial investment, the returns substantially outweigh the costs, with positive ROI expected within the first year of full implementation.
5. Benefits & Risks
Benefits
- Development Speed – Studies indicate that AI-assisted coding can already improve developer productivity by 20-80%, allowing teams to release software significantly faster. We believe this is only going to rapidly accelerate further. This acceleration enables more rapid response to market changes and customer feedback, creating a more agile organisation.
- Cost Efficiency – AI-assisted development reduces manual coding effort, leading to lower development costs and improved resource allocation.
- Product Success Rate – AI-driven development enables rapid prototyping and iteration, improving the ability to validate and adapt products in real-time, and leading to higher customer satisfaction and better product-market fit.
- Talent Attraction and Retention – Offering cutting-edge AI development environments helps attract top technical talent while providing existing staff with growth opportunities in emerging technologies, addressing recruitment challenges in today's competitive market.
Risks & Mitigation Strategies
- Staff Attrition & Morale Impact – Transitioning to Enterprise Vibe may create uncertainty among existing employees who fear job displacement.
- Focus on upskilling and AI empowerment, framing AI as an augmentation tool rather than a replacement. Provide career path guidance to demonstrate opportunities in an AI-driven environment.
- Implement clear communication and engagement strategies to reassure staff about career progression in an AI-driven environment.
- Governance & Compliance Risks – AI-generated code must align with enterprise security, legal, and regulatory requirements.
- Embed AI governance frameworks, establish best practices for AI-assisted development, and implement continuous monitoring for compliance.
- Initial Learning Curve & Adoption Resistance – Teams unfamiliar with AI-driven workflows may struggle with the transition.
- Provide structured AI training, pilot programs, and success showcases to drive adoption. Offer mentorship programs pairing experienced AI developers with those new to the technology.
- Data Security & Privacy Concerns – Using AI models involves data sharing, which could lead to potential breaches or compliance issues if not handled carefully.
- Implement robust data governance policies, anonymisation techniques, and secure AI development environments. Regularly audit AI systems for vulnerabilities.
- Vendor Dependency – Reliance on specific AI providers could create lock-in and business continuity risks.
- Develop a multi-vendor strategy with standardised interfaces and contingency plans for service disruptions.
6. Competitive Analysis
Enterprise Vibe positions organisations favourably against competitors in several dimensions.
Competitive Advantages of Implementation
- First-mover advantage in our specific market segment
- Ability to deliver features and products 20-80% faster than competitors
- Enhanced ability to respond to changing market conditions
- Higher developer productivity leading to more innovation capacity
Competitive Risks of Inaction
- Increasing gap in development velocity compared to early adopters
- Difficulty attracting top technical talent who seek AI-enhanced environments
- Higher development costs compared to competitors using AI tools
- Reduced ability to respond quickly to market changes
This analysis demonstrates that implementing Enterprise Vibe provides significant competitive advantages in our market, while delaying implementation creates increasing competitive risk as industry adoption accelerates.
7. Target Operating Model - Teams & roles
Enterprise Vibe has built its operating model from the ground up, considering what is truly required in an AI-driven world. At its core, small, agile 'Vibe Teams' - comprising a GTM Engineer, a Product Lead, and an Engineer - collaborate closely, leveraging AI tools to rapidly prototype, test, and deploy solutions within a structured 5-day cycle. These teams operate autonomously but are supported by a centralised expert network ensuring security, compliance, infrastructure alignment, and governance based on the PESTEL framework.
Vibe Teams
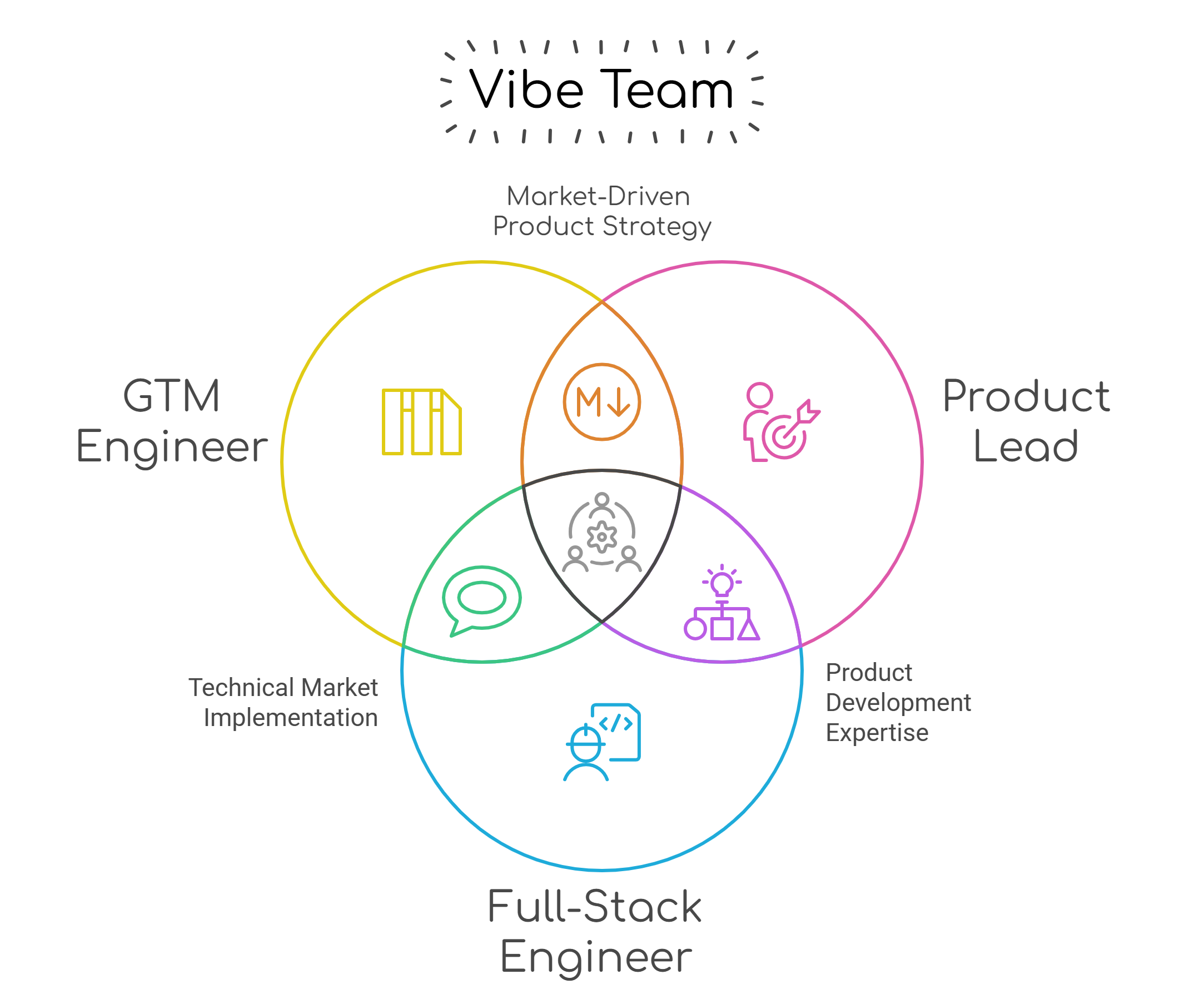
Each Vibe Team consists of three core roles:
- GTM Engineer – Owns go-to-market strategy, client engagement, account management, and support. They have primary accountability for sales, ensuring revenue growth and client acquisition.
- Product Lead – Primary user to interface with AI tools to drive development, validate outputs, and iterate on solutions with a focus on UX. This role combines domain expertise with AI interaction skills to direct the development process effectively.
- Full-Stack Engineer – Ensures AI-generated code is secure, scalable, and integrates with enterprise infrastructure; focuses on aspects AI cannot fully automate yet (e.g., security, DevOps, and performance optimisation). Also responsible for maintaining and updating AI models with new data and feedback.
Each Vibe Team operates autonomously but has access to centralised expert support when needed, creating a balance between empowered independence and enterprise consistency.
Centralised Expert Support
A key function of centralised expert support ensures that Vibe Teams operate within a structured framework that aligns with the broader business landscape.
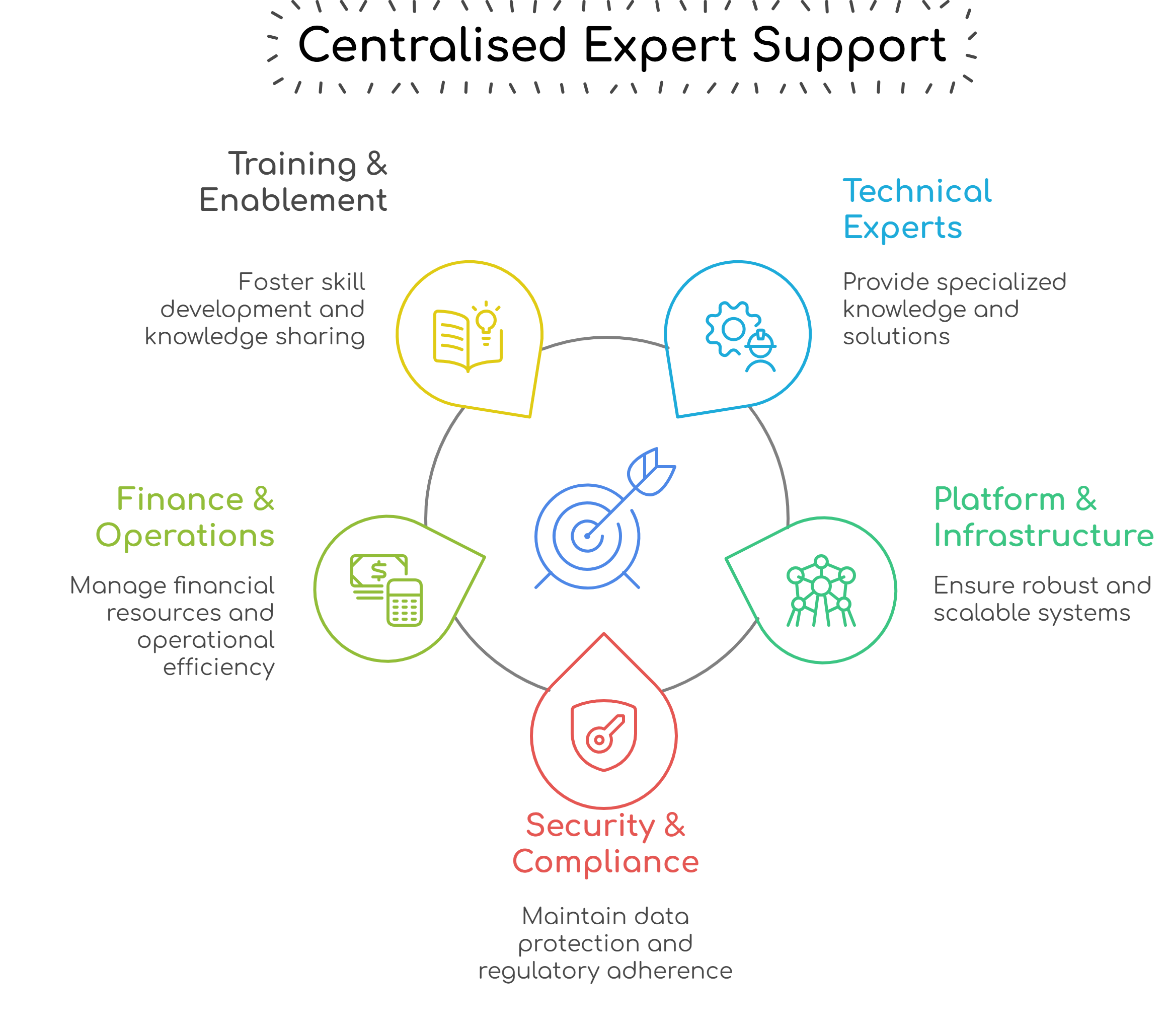
These expert functions include:
- Technical Experts – Specialised engineers and AI specialists available to all teams for deep technical challenges and advanced AI model customisation.
- Platform & Infrastructure – Manages core enterprise architecture, ensuring AI development aligns with enterprise standards, and provides scalable AI infrastructure.
- Security & Compliance – Embeds governance without blocking velocity, monitors AI systems for vulnerabilities, and ensures data privacy.
- Finance & Operations – Supports pricing models, cost control, resource allocation, invoicing and ROI tracking.
- Training & Enablement – Develops and delivers comprehensive training programs to upskill employees on human skills and Enterprise Vibe methodologies.
These central teams ensure standardisation, compliance, efficiency, and knowledge sharing across all Vibe Teams.
These teams require individuals that have strong understanding and skillsets related to PESTEL framework, ensuring that developments consider:
- Political – Compliance with government regulations, AI governance policies, and geopolitical considerations affecting software deployment and data handling.
- Economic – broader economic outlook, cost efficiencies, budget allocations for tooling, long-term financial sustainability, and assessing the ROI of initiatives.
- Social – Workforce impacts, ethics including ethical AI usage, customer acceptance of AI-driven products, and addressing potential biases in AI outputs.
- Technological – Trend trends, maintaining competitive advantage, ensuring compatibility with evolving enterprise tech stacks, and exploring emerging technologies.
- Environmental – Sustainable computing, energy-efficient AI models, corporate responsibility initiatives, and reducing the carbon footprint of operations.
- Legal – Adherence to laws including AI compliance, data privacy regulations, intellectual property considerations, and ensuring data sovereignty.
Communication is key
High-level of communication is vital to ensure consistency and alignment across Vibe Teams as well as joined up messaging to clients & prospects.
Don't wait!
Continuous communication is the backbone of Enterprise Vibe. Waiting for scheduled meetings to address issues or share insights will slow progress. Instead, communication should be proactive and real-time, using collaboration tools like Slack and Notion to flag and resolve challenges immediately. Encourage team members to reach out across teams when misalignments or dependencies arise, and ensure updates and decisions are shared openly with all relevant stakeholders.
To maintain momentum and prevent silos, make work visible and foster a culture of ongoing feedback and iteration. Rather than waiting for scheduled reviews, address challenges as they come up and refine strategies dynamically. Proactively engage with clients, prospects, and partners, providing them with timely updates. Similarly, ensure alignment across teams such as marketing, sales, and support for consistent messaging. By embedding continuous communication, Enterprise Vibe can drive agility, collaboration, and a unified approach to both internal and external interactions.
Internal communication
Transparent AI adoption policies, regular showcases of AI-driven successes, structured training programs, and open forums for addressing employee concerns and feedback. The internal communication approach will emphasise how Enterprise Vibe enhances developer capabilities rather than replacing human expertise.
- Enterprise Vibe Council – A cross-functional leadership group that meets weekly to review progress, resolve roadblocks, ensure teams align with business objectives, and assess the ethical implications of AI implementations.
- Weekly Vibe Team Syncs – Short alignment meetings where multiple vibe teams share updates, discuss dependencies, flag blockers, and identify opportunities for cross-team collaboration to maintain momentum.
- Monthly Strategy Reviews – A broader forum analysing trends, refining methodologies, ensuring AI tool usage aligns with business strategy, and reviewing key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Quarterly Enterprise AI Audits – A deep-dive review of AI-generated outputs, ensuring compliance, security, performance benchmarks are met, and identifying areas for process improvement.
External communication
Vibe teams are responsible for defining and executing their own go-to-market (GTM) and support strategies while ensuring alignment with other teams and centralised experts. To maintain consistency and collaboration, teams should adopt the following strategies:
Cross-Team Communication & Collaboration
- Regular syncs & stand-ups to share updates and align strategies.
- Cross-team liaisons to facilitate communication between vibe teams and expert groups.
- Shared workspaces (e.g., Notion, Slack) for transparent documentation of plans and insights.
Consistency in Go-to-Market Execution
- GTM frameworks & playbooks to provide adaptable yet standardised best practices.
- Coordinated launch planning to prevent overlap and ensure cohesive messaging.
- Internal demos & testing to refine messaging and gather feedback before launch.
Unified Support Strategy
- Centralised knowledge base for FAQs and best practices.
- Standardised SLAs & escalation paths to maintain customer service consistency.
- Rotational support duty to reinforce team ownership of customer experience.
Engaging Centralised Expert Teams
- Advisory & review boards to validate major GTM and support plans.
- Embedded specialists to provide hands-on guidance during critical phases.
- Training & enablement to keep teams aligned with compliance and best practices.
Metrics & Continuous Improvement
- Shared KPIs (e.g., adoption, churn, NPS) to ensure unified goals.
- Retrospectives & post-mortems to analyse GTM launches and support incidents.
- Cross-team feedback loops (e.g., town halls, office hours) to refine strategies collaboratively.
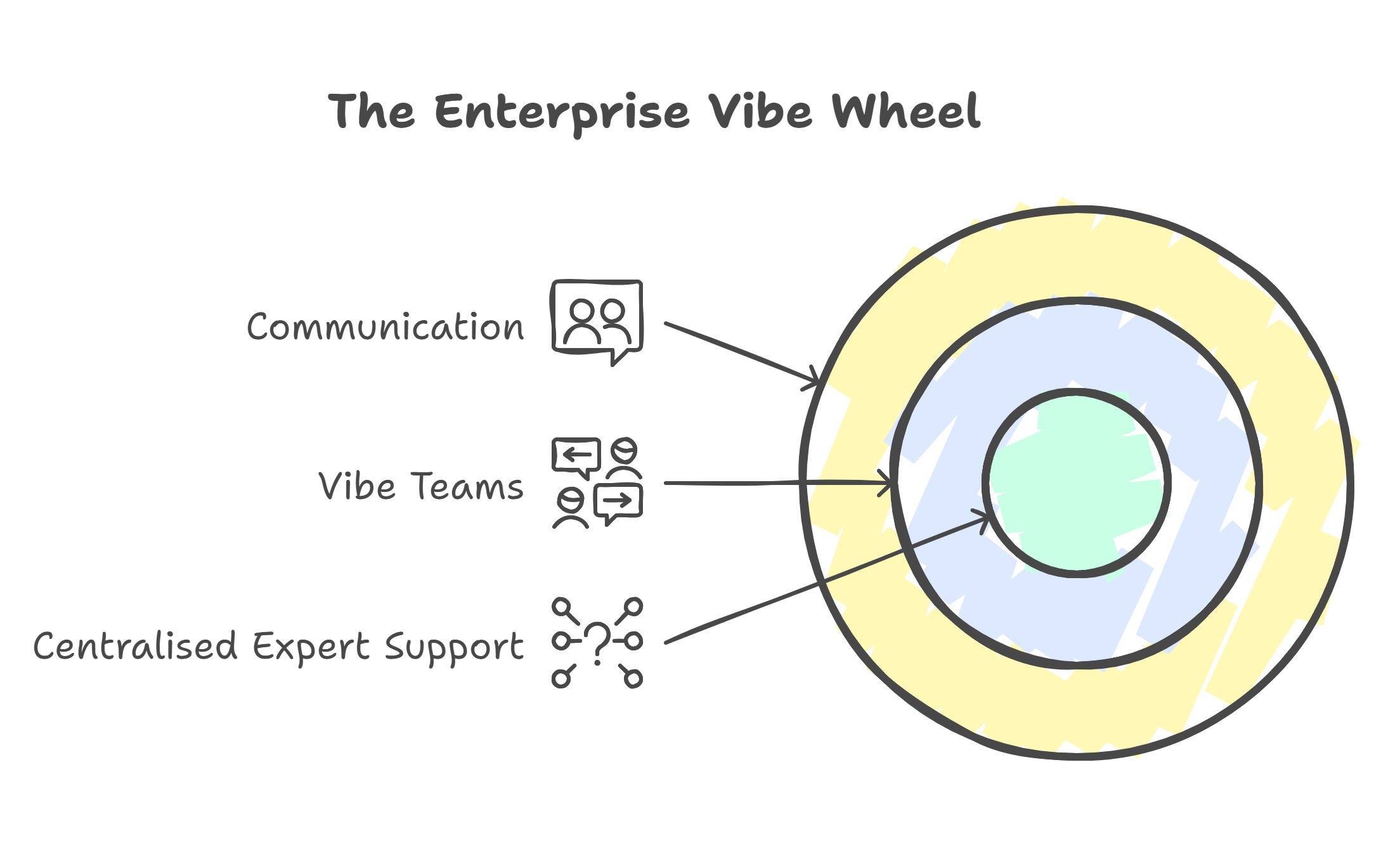
The Enterprise Vibe wheel
The visual below provides a straightforward representation of the Target Operating Model. It serves as a guide for explaining the concept and can also inform the design of both digital and physical spaces to align with an Enterprise Vibe environment.
8. Colocation
Colocation - whether physical or virtual - is highly recommended as it enhances communication, speeds up decision-making, and strengthens team cohesion.
The Benefits
- Faster problem-solving – Real-time discussions help teams quickly resolve issues and align priorities.
- Stronger collaboration – Spontaneous interactions foster creativity, while structured teamwork keeps AI-driven workflows on track.
- Greater adaptability – Close-knit teams can pivot quickly when priorities shift.
- Improved transparency – Shared workspaces ensure visibility, reducing silos and keeping teams aligned.
How to Do It Well
- Create collaborative spaces – Open office layouts and digital tools (e.g., Teams, Slack, Miro) keep teams connected.
- Hold daily syncs – Quick check-ins ensure alignment and refine AI-generated outputs.
- Use dedicated team spaces – Whether physical or virtual, teams need a shared environment to collaborate effectively.
- Provide expert support – A centralised governance and security team should be on hand to assist without slowing progress.
- Encourage openness – Regular feedback loops and knowledge sharing strengthen team dynamics.
Colocation isn't just about proximity—it's about ensuring teams work seamlessly together, whether in person or remotely, to maximise the benefits of AI-driven development.
9. Target Operating Model - Delivery process
5-Day Vibe Cycle
Traditional Agile follows a two-week sprint cycle, typically resulting in partial product increments rather than full feature delivery. Enterprise Vibe introduces a 5-Day Vibe Cycle designed to rapidly deliver complete products or features:
- Day 1 & 2 – Build Phase: The Vibe Team collaborates intensively to create the product or feature, leveraging AI tools for rapid development and continuous testing.
- Day 3 – QA & Expert Validation: Centralised experts review security, scalability, compliance, performance aspects, and AI model accuracy to ensure enterprise-grade quality. Vibe team members test, resolve identified issues and prepare for deployment.
- Day 4 – Go-Live & Communication: Deployment to production. Structured internal and external communication to clients, prospects, and stakeholders. Monitor system performance and gather user feedback post-deployment.
- Day 5 – Learning & Retrospective: A full day dedicated to reflection, knowledge-sharing, identifying lessons learned, and improving future cycles. This ensures continuous growth, AI optimisation, enhanced product iterations, and better team collaboration.
Discovery & Ideation Process
To maintain a steady pipeline of high-impact work, Enterprise Vibe employs a structured Discovery & Ideation Process to collect, evaluate, and prioritise Enterprise scale ideas and problem statements.
1. Idea Collection & Problem Definition
- Open Submissions: Teams, stakeholders, and clients can submit ideas or problem statements through a structured intake process (e.g., dedicated forms, AI-assisted brainstorming sessions, or backlog refinement workshops).
- User & Market Research: Insights from user feedback, analytics, and market trends inform problem identification.
- AI & Data-Driven Insights: Automated trend analysis highlights common challenges and opportunities.
2. Centralised Prioritisation & Refinement
- Cross-Functional Review Board: A central team composed of representatives from Vibe Teams, product, engineering, and business functions evaluates and prioritises ideas.
- Impact vs. Effort Assessment: Each idea is scored based on business impact, feasibility, AI-enhancement potential, and strategic alignment.
- Rapid Prototyping & Validation: Selected ideas undergo quick prototyping to assess viability before entering development.
3. Roadmap Integration & Execution
- Backlog Integration: Approved ideas are integrated into the product roadmap, aligned with the 5-Day Vibe Cycle.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Regular syncs ensure prioritised ideas meet business needs and technical feasibility.
- Continuous Pipeline Management: The prioritisation process is iterative, ensuring agility in response to changing market demands.
By embedding a structured Discovery & Ideation Process, Enterprise Vibe ensures a continuous flow of high-value initiatives, balancing rapid delivery with strategic foresight.
Start up Artifacts
Core Essentials
These are the foundational elements that every development project should have in place before work begins:
- Mission Statement & Goals – A clear explanation of why the project exists and what it aims to achieve.
- Preferred Tech Stack – The frameworks, tools, and third-party services being used.
- Architecture & Integrations – A high-level system design, including APIs and dependencies.
- Project Roadmap & Milestones – A timeline outlining key phases, deliverables, and checkpoints.
- Design System & UX Guidelines – Core design principles, components, and accessibility considerations.
- Development & Deployment Process – Version control, CI/CD setup, and testing approach.
- Security & Compliance Considerations – Data handling, authentication, and regulatory requirements.
- Collaboration & Tooling Setup – The platforms used for documentation, communication, and task management (e.g., Slack, Notion, Jira, GitHub).
Other Recommendations
Beyond the essentials, teams can improve efficiency and long-term maintainability by setting up additional frameworks and workflows:
- Team Profiles & Work Preferences – A shared reference capturing preferred collaboration styles, availability, and communication preferences.
- AI Usage Strategy – Defining how AI tools (e.g., Copilot, ChatGPT, Figma AI) will be used for coding, documentation, and automation.
- Ethical AI & Bias Considerations – Guidelines to ensure responsible AI use, particularly in automated decision-making.
- Adaptive Design System – A design framework that supports personalization, theme switching, and accessibility improvements.
- Project Anti-Goals – A list of things to avoid, such as unnecessary complexity, scope creep, or reliance on proprietary vendor lock-in.
- Knowledge Base with AI Search – A central repository for documentation, enhanced with AI-powered search to improve accessibility.
- AI-Assisted Tech Debt Tracking – A structured way to document and prioritise technical debt, leveraging AI for risk assessment.
- Prompt Library for AI Collaboration – A collection of useful AI prompts for debugging, brainstorming, and documentation assistance.
10. Implementation: Parallel Approaches
The implementation of Enterprise Vibe follows a structured, phased approach designed to manage change effectively while demonstrating value early. This transformation operates on two parallel tracks:
Strategic Transformation (10x) – Enterprise Vibe: A full-scale shift towards AI-empowered, high-velocity development methodologies, built around dedicated Vibe Teams.
Tactical Augmentation (10%) – AI in Current Workflows: A pragmatic, incremental approach where existing teams integrate AI-driven development tools, such as GitHub Copilot, to enhance productivity within current ways of working.
By running these approaches in parallel, we ensure immediate, tangible improvements while gradually evolving towards Enterprise Vibe.
Strategic Transformation (10x) – Enterprise Vibe
A structured, phased approach to fully embed AI-powered Vibe Teams within the organisation:
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-3)
- Establish governance framework and policies.
- Select and implement initial AI tooling.
- Develop training materials and programs.
- Identify pilot Vibe Teams and projects.
- Define metrics and baseline measurements.
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 4-6)
- Launch 3-5 pilot Vibe Teams.
- Train initial team members.
- Execute 2-3 pilot projects.
- Measure outcomes and gather feedback.
- Refine processes and approaches.
Phase 3: Scaled Adoption (Months 7-12)
- Standardise training and onboarding.
- Create detailed plans for legacy products/processes.
- Implement refined governance processes.
- Establish communities of practice.
- Begin measuring ROI and business impact.
Phase 4: Enterprise Integration (Months 13-24)
- Fully integrate Enterprise Vibe with business processes.
- Optimise tooling and methodologies.
- Develop advanced capabilities and custom models.
- Formally establish centers of excellence.
- Scale to organisation-wide adoption.
This phased approach ensures controlled implementation, learning, and adaptation while demonstrating value early to build organisational support.
Tactical Augmentation (10%) – AI in Current Workflows
A complementary approach to drive immediate efficiency gains by leveraging AI within existing processes:
Phase 1: AI Awareness & Enablement (Months 1-3)
- Identify and introduce AI-assisted development tools (e.g., GitHub Copilot).
- Provide introductory training and workshops.
- Encourage voluntary adoption among teams.
- Define success metrics for AI-assisted development.
Phase 2: AI-Assisted Development (Months 4-6)
- Support teams in integrating AI tools into daily workflows.
- Monitor and document efficiency gains.
- Establish knowledge-sharing forums.
- Collect feedback to refine AI adoption strategies.
Phase 3: Process Optimization (Months 7-12)
Phase 3: Process Optimisation (Months 7-12)
- Identify best practices and success stories.
- Expand AI-assisted development to additional teams.
- Begin structured tracking of AI-driven productivity improvements.
- Align AI-augmented work with broader Enterprise Vibe goals.
Phase 4: AI-Driven Excellence (Months 13-24)
- Define AI governance standards for long-term integration.
- Optimise AI-assisted workflows for maximum efficiency.
- Develop tailored AI-assisted development strategies for different teams.
- Establish AI champions to continuously drive adoption and refinement.
11. Key Performance Indicators
Success of the Enterprise Vibe implementation will be measured through the following key metrics:
Development Velocity Metrics
- Time-to-market for new features (target: 30-40% reduction)
- Development cycle time (target: 50% reduction)
- Code generation efficiency (AI-generated code percentage)
- Iteration frequency (number of product iterations per time period)
Quality Metrics
- Defect density in production code (target: 20% reduction)
- Security vulnerability identification (target: 90% pre-production detection)
- Test coverage (target: 95% of critical functionality)
- Post-release incident frequency (target: 30% reduction)
Business Impact Metrics
- Feature delivery rate against roadmap (target: 30% increase)
- Cost per feature delivered (target: 25% reduction)
- Customer satisfaction with product quality (target: 15% improvement)
- Revenue impact from accelerated feature delivery
Organisational Metrics
- Developer satisfaction and engagement scores
- AI tool adoption rates across development teams
- Developer productivity (features delivered per developer)
- Training completion and effectiveness measures
These KPIs will be tracked from the beginning of implementation, with baseline measurements established during Phase 1 to enable accurate tracking of improvements.
12. Change Management Strategy
Successfully implementing Enterprise Vibe requires a comprehensive change management approach addressing cultural, skill, and process dimensions:
Leadership Alignment & Sponsorship
- Executive sponsor identified
- Leadership training on AI-assisted development benefits and implementation approach
- Regular executive updates on progress and outcomes
- Visible leadership participation in key events and communications
Communication Plan
- Tailored messaging for different stakeholder groups
- Regular town halls and Q&A sessions
- Success stories and case studies from pilot implementations
- Clear articulation of "what's in it for me" for affected employees
Training & Enablement
- Role-based training programs for all affected staff
- Hands-on workshops with AI coding tools
- Certification program for Enterprise Vibe practitioners
- Communities of practice for ongoing learning
Feedback & Adaptation Mechanisms
- Regular surveys to assess adoption and identify barriers
- Feedback channels for implementation suggestions
- Adaptation of approach based on ongoing learning
- Recognition programs for successful adoption
Cultural Transformation
- Shift from "code writing" to "solution engineering" mindset
- Emphasis on collaboration and knowledge sharing
- Recognition of AI partnership rather than replacement
- Celebration of early successes and learning
This comprehensive change management approach addresses the human aspects of the transformation, which are often more challenging than the technical implementation.
13. Talent Strategy
Supporting talent in Enterprise Vibe requires a shift from traditional hiring & training approaches, prioritising adaptability, collaboration, and AI fluency to build high-performing Vibe Teams.
Collaboration & Communication Skills
Essential for Vibe Teams to function effectively in a dynamic, AI-driven environment. Recruitment processes will be updated to assess these skills effectively through scenario-based interviews and collaborative exercises.
Psychometric Profiling
Ensures team chemistry, alignment with AI-driven workflows, and assesses adaptability to new technologies. A specific profile for Enterprise Vibe roles will be developed based on successful pilot team members.
Hiring as a Team
Where possible, recruiting pre-formed teams rather than individuals to maximise synergy and accelerate team integration. This approach reduces ramp-up time and leverages existing working relationships.
AI-Assisted Hiring
Using AI tools to identify high-potential candidates based on adaptability, problem-solving skills, and continuous learning capabilities. This approach broadens the candidate pool while identifying those most likely to succeed in an AI-enhanced environment.
T-shaped People
T-shaped People Enterprise Vibe relies on T-shaped people - individuals with deep expertise in their craft and a broad ability to collaborate across disciplines - ensuring agility, innovation, and seamless teamwork in a fast-moving environment. A T-shaped person possesses both depth and breadth of skills. The vertical bar of the "T" represents deep expertise in a specific domain, while the horizontal bar signifies a broad understanding across multiple disciplines. This combination allows T-shaped individuals to excel in their area of specialisation while effectively collaborating across different fields. They can communicate with experts from various backgrounds, adapt to different challenges, and contribute meaningfully beyond their core skill set. In modern organisations, T-shaped people are highly valued because they bridge gaps between teams and drive innovation. For example, a software engineer with deep knowledge of back-end development (the vertical bar) but also a strong grasp of user experience, business strategy, and team leadership (the horizontal bar) can help create more user-centric products while aligning technical decisions with business goals. Encouraging a workforce of T-shaped individuals fosters agility, collaboration, and adaptability - key traits that underpin Enterprise Vibe and enable organisations to thrive in complex and fast-paced environments.
Wild Card People
While T-shaped individuals provide a balance of depth and breadth, wild card people bring unpredictability, unconventional thinking, and a knack for seeing opportunities others overlook. A wild card person is someone who doesn't fit neatly into predefined roles but thrives on adaptability, creativity, and disruption. They often have a mix of skills and experiences that defy traditional categorisation, making them difficult to place within standard organisational structures.
Wild card people challenge assumptions, question established processes, and introduce fresh perspectives that can lead to breakthrough ideas. They are often generalists with deep expertise in unexpected areas or specialists who apply their knowledge in unconventional ways. They might switch industries, blend disciplines, or operate outside traditional hierarchies, making them invaluable connectors and problem-solvers.
In Enterprise Vibe, these individuals are essential for injecting energy, innovation, and strategic surprises. They may not follow traditional career paths or structured workflows, but their ability to connect disparate ideas, pivot quickly, and thrive in ambiguity makes them powerful assets—when given the right environment to flourish.
14. Resource Requirements
Successful implementation of Enterprise Vibe requires the following resources:
Resource Requirements
- Full-time implementation team: 6 FTEs for 12 months
- Executive sponsor: 10% time commitment
- Expert support: 20% time commitment each
Budget Requirements
- AI tooling licenses: £tbc annually
- Infrastructure enhancements: £tbc initial investment
- Training and enablement: £tbc in year one
- Change management and communication: £tbc
Infrastructure Requirements
- AI model training and hosting capabilities
- Secure AI development environments
- Integration points with existing development tools
Governance Requirements
- Enterprise Vibe Council establishment and operation
- Policy development and implementation
- Compliance monitoring systems
- Performance management frameworks
These resource requirements represent the investment necessary to achieve the substantial benefits outlined in the business case, with the expectation of positive ROI within the first year of full implementation.
15. Tooling for Enterprise Vibe
The following are just a few examples of AI-powered tools that can support Enterprise Vibe. As technology evolves, new tools will continue to emerge, shaping how teams work and collaborate:
Bolt.new
AI-powered coding assistant for product development that enables rapid code generation through natural language descriptions and intent specifications.
Cursor
AI-assisted code generation and debugging with enhanced code completion features that significantly reduce the manual effort required for implementation.
Anthropic Claude & OpenAI GPT
Large language models for code generation and refinement, supporting multiple programming languages and providing versatile capabilities for various development tasks.
AI-powered QA & Security Tools
Automated vulnerability detection, AI-assisted testing platforms, and real-time code analysis that identify and remediate potential issues before they reach production.
Data Visualisation Tools
Tools like Tableau or Power BI to visualise and monitor the performance of AI models and Vibe team productivity.
AI Model Monitoring Platforms
Platforms to track the accuracy, fairness, and reliability of AI models in production.
16. First Steps
Upon approval of this proposal, the following immediate actions will be taken:
- Obtain executive buy-in (Week 1)
- Establish the Enterprise Vibe implementation team and executive sponsor (Week 1-2)
- Finalise the detailed implementation plan and resource allocation (Week 2-4)
- Select and procure initial AI tooling for pilot implementation (Week 3-6)
- Identify pilot teams and projects for initial implementation (Week 4-6)
- Develop and begin delivering initial training programs (Week 5-8)
- Launch the first pilot project using the Enterprise Vibe methodology (Week 8-10)
These steps will initiate the implementation process while allowing for appropriate planning and preparation to ensure successful execution.
17. Vision of the Future
Imagine a future where the very concept of a "product" is fundamentally challenged due to the pace of which software can be developed. Enterprise Vibe is the first step toward a world where software is no longer a static, pre-packaged entity, but rather a fluid, adaptive, and highly personalised experience.
The Death of "One-Size-Fits-All"
In the future enabled by AI-driven development, generic products become obsolete. Customers demand and receive hyper-personalised solutions tailored to their unique needs, preferences, and contexts. Products are built to exact client needs, not generic for entire markets.
Minutes to Market
The speed of AI-assisted development reduces time-to-market from months or years to mere minutes. A client's problem can be translated into a working, customised solution almost instantaneously, removing the friction and delays of traditional development cycles.
Dynamic Skillsets
The role of the "developer" evolves beyond coding proficiency. Human skills shift toward creative problem-solving, AI collaboration, complex system design, ethical oversight, and nuanced communication. The ability to articulate intent, manage AI outputs, and understand user needs becomes paramount.
The Algorithmic Enterprise
Business models transform. Instead of selling products, companies offer adaptive solutions that continuously learn and evolve based on user interactions. Businesses become algorithmic entities, dynamically reconfiguring themselves to meet ever-changing customer needs.
The Empowered User
Users become active participants in the development process. Through natural language interfaces and AI-driven feedback loops, they directly shape the evolution of their software, creating a symbiotic relationship between user and system.
Beyond Products, Experiences
The focus shifts from delivering features to crafting holistic user experiences. Software becomes an invisible layer, seamlessly integrating into people's lives and anticipating their needs before they even arise.
The Ethics Imperative
As AI takes on a more prominent role in development, the ethical considerations become critical. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems becomes a core competency, requiring careful governance and oversight.
Enterprise Vibe is not just about faster coding; it's about unlocking a fundamentally new paradigm in software development - one where software is hyper-personalised, dynamically adaptive, and ethically driven. Embracing this vision requires a bold shift in mindset, but the potential rewards are transformative.
18. Appendix: Sources
Coming soon